Frequently asked questions (FAQ)¶
- What is Opendatasoft?
Opendatasoft is a turnkey SaaS platform developed for business users to easily share, publish and reuse structured datasets.
- Is Opendatasoft open source?
Opendatasoft is not open source.
Opendatasoft is selling a service, not a software. However, some parts of the stack are open source.
Opendatasoft’s front-end is open source. It is built and packaged as a set of AngularJS directives. This project can be accessed on GitHub and comes with a full fledged documentation.
Opendatasoft is also already contributing to the Elasticsearch project by releasing in the public space a set of plugins that we have developed and that we use internally:
- Is the Opendatasoft team managing data on behalf of its customers?
No.
Opendatasoft sells a turnkey solution. Users manage their datasets on their domains by themselves. Of course, the Opendatasoft support team is more than willing to help handling complex / specific data management issues.
Moreover, Opendatasoft maintains a data network which federates public datasets published by Opendatasoft customers as well as datasets published by the Opendatasoft staff.
- I’m representing a public administration. My country has already setup an Open Data initiative. Why should I have my own data portal?
Open Data is about making data that has been produced by public administrations available to citizens. But most of the time, one may want to go beyond the simple delivery of raw files and:
- Contextualize & increase the value of data
- Make data easy-to-understand for citizens
- Provide open services to an ecosystem of developers / reusers
To that extent, having a data management tool tailored to your needs is mandatory and keep in mind that thanks to the Open APIs provided by Opendatasoft, your national Open Data portal will always have the possibility to reference your public datasets.
- If I publish datasets on Opendatasoft, will they automatically be available to everyone on the Web?
No.
The Opendatasoft platform can be used for both public and private data management projects. A given platform can even host public and private datasets. It is also possible to define the ACL of a recordset at the dataset level.
- What file formats are supported by Opendatasoft?
The Opendatasoft platform natively supports the following file formats:
CSV``GeoJSONJSONJSON linesKMLOSM archives (OpenStreetMap)ShapefileMapInfoExcelOpenDocument SpreadsheetRemotely stored files for any of the above formats (HTTP or FTP)
Specific format parsers can also be made available by the Opendatasoft team for specific requirements.
The Opendatasoft platform is also able to connect to remote Web services. Opendatasoft supports the following services in its standard version:
ArcGIS REST APIRSS / Atom feedsSalesforce / Force.com(you’ll have to ask Opendatasoft support to activate it on your domain)
Custom connectivity capabilities can be added upon request.
- What metadata standards does Opendatasoft support?
Opendatasoft natively uses a subset of DCAT to describe datasets. The following metadata are available by default:
titledescriptionlanguagethemekeywordlicensepublisherreference
It is possible to activate the full DCAT template, thus adding the following additional metadata:
createdissuedcreatorcontributoraccrual periodicityspatialtemporalgranularitydata quality
A full INSPIRE template is also available and can be activated on demand.
The metadata template can be customized (adding custom metadata). To do so, simply issue a support request from your Opendatasoft’s back-office.
- How many datasets can I create?
You can create as many datasets as you want within the limit set in your licensing plan.
- How could I modify the look & feel of my Opendatasoft domain?
As a domain administrator, you can fully customize the styling of your portal. Logos, pictos, colors, styles as well as the header, the footer and the dataset box layout in the catalog page can be fully customized.
- How can other people collaborate on dataset configuration?
Use the security section in your dataset’s configuration page in Opendatasoft’s back-office to give other users or groups of users a write access to the dataset. These users should also have access to your domain to access your dataset. If this is not the case already, you should contact your domain administrator.
- How can I transform and enrich my datasets?
A rich set of processing features is made available in the publishing console. Simply hit the Add Processor button.
- Can I geocode a full-text address?
Yes.
Opendatasoft supports Google and ESRI geocoding services. However, Opendatasoft doesn’t come with geocoding API keys. The domain administrator has to configure a geocoding API key for one of these services in the back-office configuration (Configuration > Data processing).
- I have geocoded data in my dataset but the map view doesn’t display anything. What went wrong?
Remember that you dataset must contain at least a field of type Geo Point or Geo Shape
- Geo Point:
latitude,longitudein WGS84, e.g.:48.2567,3.7689. - Geo Shape: any valid Geo JSON geometry in WGS84
- What is a facet?
Facets are the backbone of most of the features made available by the Opendatasoft platform. A facet is simply a field which has been given specific filtering and aggregation capabilities.
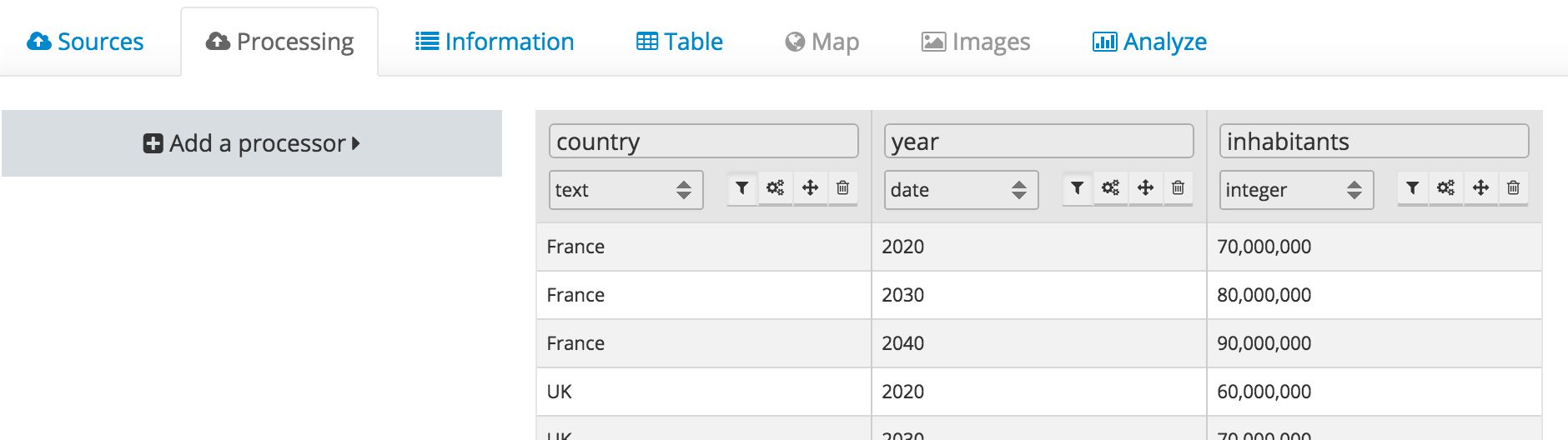
In the example above, the fields country and year have been defined as facets (notice the filter button next to the type select).
Facets can be seen as dimensions of a dataset. Facets can be defined on the following field types:
datedatetimetextintdecimal
Facets shall only be configured for fields that have a small number of different values compared to the number of records in a dataset. For instance, defining a facet on an field that would uniquely identify a record is useless as filtering on this field wouldn’t bring any added value.
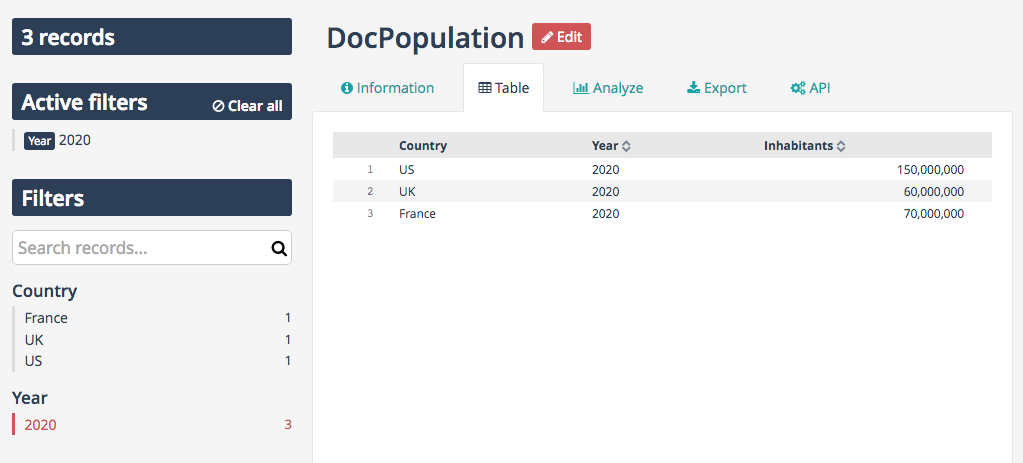
Facets are then used in a couple of places.
You can first use them to filter dataset records in the explore console.
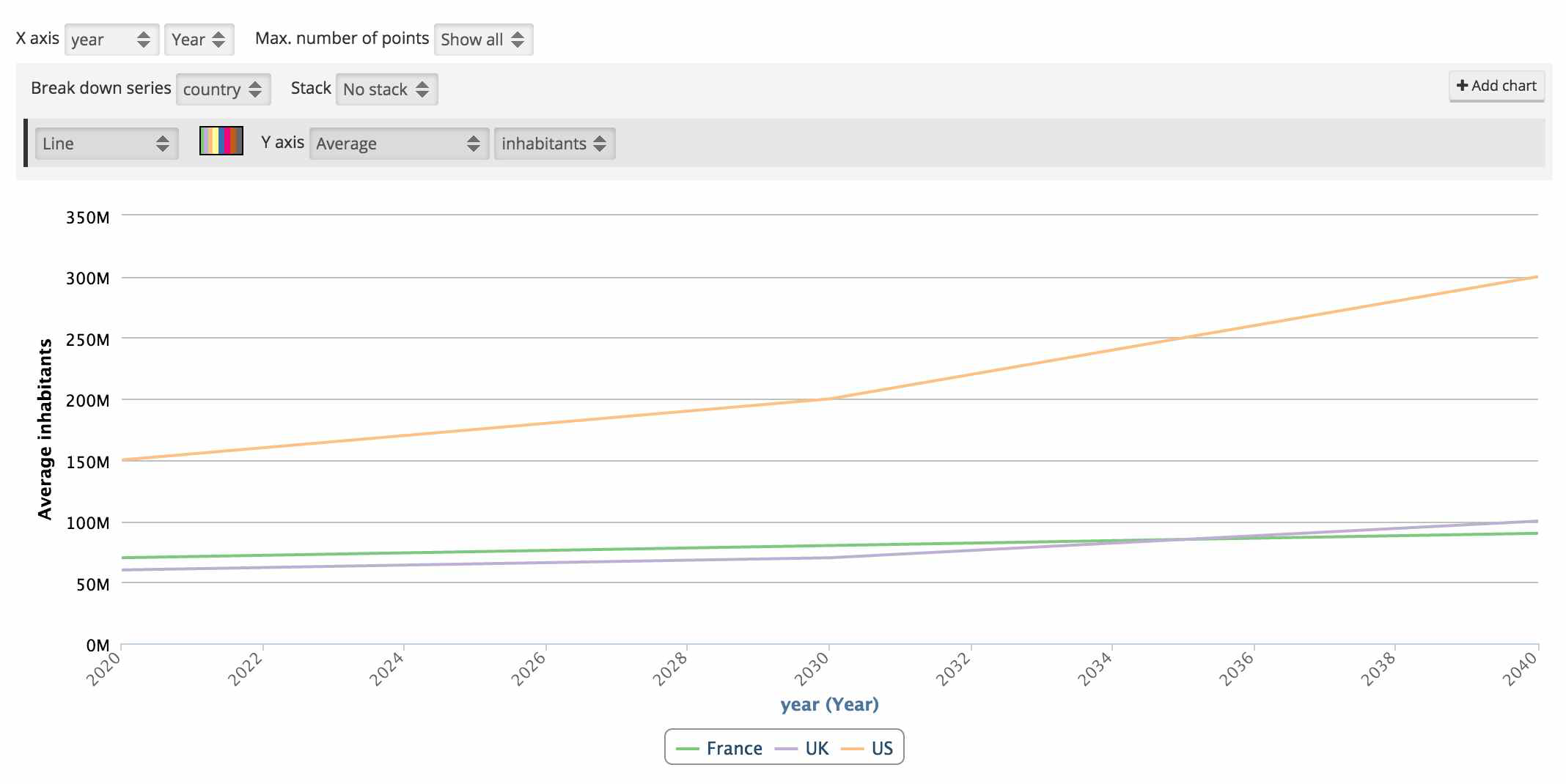
As dimensions, facets support aggregations. You can thus use them to build advanced charts, as in the example below.
- I have an Opendatasoft free trial account, how can I get a premium account?
Please send a message to <contact@opendatasoft.com>.
We will be happy to discuss your needs and to propose you one of our plans.
- How can I display points on a map?
For a geo data visualization to be available, your dataset needs to contain a Geo Point 2D field with content in
the latitude,longitude format. For instance: 48.2567,3.7689.
- In the table view, I have not been able to sort the results using a specific field? What went wrong?
By default, only the numerical fields are sortable. That is, fields having one of the following types:
intdoubledatedatetime
Text fields are not sortable by default. The dataset owner may configure some text fields to be sortable. Sortable text fields can be identified through the API (sortable annotation).
- I published a dataset, but no category is displayed in the left column. What shall I do?
Categories (facets) are built out of fields which have been defined as a facet. To set a field as a facet, simply click on the filter icon, in the field definition header in the publishing console.
- When I go to the analyze view, the displayed chart doesn’t make any sense. How could I change this?
The dataset owner can easily define the default analytical representation of the dataset using the analyze tab in the publishing console. End-users can also simply choose different settings and build their own analytical data visualization using the available controls.
- How can I embed a data visualization on my website?
There are three ways to embed Opendatasoft’s data visualizations on a website or any content management system:
- Copy-paste the embed code that can directly be found on the Opendatasoft platform (usually located under the data visualization itself).
- Use ODS Widgets, our open source widget library to build content pages tailored to your needs with one or several data visualizations at once.
- Use Opendatasoft’s HTTP/REST APIs to develop your own embed.
- What is “Cartograph”?
Cartograph is a tool developed by Opendatasoft to make it possible to build geo mashups out of datasets stored on the Opendatasoft platform.
- What does API mean?
API is an acronym for Applications Programming Interface. An API is a set of methods for computer programs to exchange information in an autonomous way. Opendatasoft APIs allow for remote access to datasets using the HTTP protocol.
- What are APIs made for?
APIs are a set of tools that developers can use to integrate data in their applications (Web applications, mobile applications, business applications...).
- How many API calls can I perform?
API endpoints are associated with quotas. Opendatasoft customers can configure their own quotas policy. Contact your Opendatasoft domain owner for more details.
- Does every dataset have its own APIs?
Yes.
Whenever you publish a dataset, a dedicated API is created. See APIs documentation for more information.
- What are the compatible browsers for Opendatasoft’s platform?
| Browser | Supported versions |
|---|---|
 Firefox Firefox |
Latest version |
 Chrome Chrome |
Latest version |
 Safari Safari |
Latest version |
 Edge Edge |
Latest version |
Glossary¶
Data glossary
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
Data |
Data is a set of values of qualitative or quantitative variables.[...]While the concept of data is commonly associated with scientific research, data is collected by a huge range of organizations and institutions, ranging from businesses (e.g., sales data, revenue, profits, stock price), governments (e.g., crime rates, unemployment rates, literacy rates) and non-governmental organizations (e.g., censuses of the number of homeless people by non-profit organizations). |
Data Model |
A Data Model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to properties of the real world. For instance, a data model may specify that a data element representing a car comprise a number of other elements which in turn represent the color, size and owner of the car. |
Data Quality |
Data quality refers to the level of quality of data. There are many definitions of data quality but data are generally considered high quality if “they are fit for their intended uses in operations, decision making and planning.” |
Open Data |
Open data is the idea that some data should be freely available to everyone to use and republish as they wish, without restrictions from copyright, patents or other mechanisms of control. The goals of the open data movement are similar to those of other “open” movements such as open source, open hardware, open content, and open access. |
Query |
A web search query is a query that a user enters into a web search engine to satisfy his or her information needs. Web search queries are distinctive in that they are often plain text or hypertext with optional search-directives (such as “and”/”or” with “-” to exclude). They vary greatly from standard query languages, which are governed by strict syntax rules as command languages with keyword or positional parameters. |
Semantic Web |
A representation in two (or possibly three) dimensions of the semantic relationships between and among terms and the concepts they represent; (ANSI/NISO Z39.19-200x). The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and community boundaries. |
Taxonomy |
A collection of controlled vocabulary terms organized into a hierarchical structure. |
Unstructured Data |
Data that is more free-form, such as multimedia files, images, sound files, or unstructured text. Unstructured data does not necessarily follow any format or hierarchical sequence, nor does it follow any relational rules. Unstructured data refers to masses of (usually) computerized information which do not have a data structure which is easily readable by a machine. |
Opendatasoft glossary
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Assets | Assets are the graphical elements uploaded to the platform. Assets can be images or fonts, they can be used on custom pages. |
| Catalog | The catalog is a register of all the dataset you have on your platform. The collection of datasets is organized and can be browsed by a full text search and filtered using the datasets’ characteristics |
Chart |
A chart, also called a graph, is a graphical representation of data, in which “the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart”. A chart can represent tabular numeric data, functions or some kinds of qualitative structure and provides different info. |
| Chart builder | Chart builder is the chart building solution of OpenDatasoft. With Chart Builder, you can choose a visualization type, choose data to display and customize X and Y axes and colors |
Choropleth map |
A choropleth map is a thematic map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the statistical variable being displayed on the map, such as population density or per-capita income. |
| Console (API) | The API console allows people to interact with the application programmable interface. The consoles offers a range of parameters to input to view the different API responses. |
| Data schema (dataset) | The data schema describes the properties attached to each fields of the records in a dataset. Data schema includes the field’s name, type and example. |
Dataset |
A dataset is an organized collection of data. The most basic representation of a dataset is data elements presented in tabular form. Each column represents a particular variable. Each row corresponds to a given value of that column’s variable. A dataset may also present information in a variety of non-tabular formats, such as an extended mark-up language (XML) file, a geospatial data file, or an image file. |
| Description (dataset) | The description is a text attached to the dataset, it allows users to understand the data inside the dataset. A good description helps users find relevant information |
Document |
A file containing Unstructured and/or Semi-Structured Data Resources. A discrete and unique electronic aggregation of data produced with the intent of conveying information. All data within a document may be in the same format (e.g., text), or a document may be a composite that consists of sets of data in a variety of formats (e.g., MS Word files containing embedded graphics). |
File format |
A file format is a standard way that information is encoded for storage in a computer file. It specifies how bits are used to encode information in a digital storage medium. File formats may be either proprietary or free and may be either unpublished or open. |
| Harvester | A harvester is an automated process to fetch data on a remote portal. The harvester fetches the datasets on a remote portal and automatically copies them to the platform. The datasets fetched can be queried with parameters. |
| Keyword (dataset) | Keywords help understand the data content of the dataset. They are used to filter, search and browse datasets by content. Keywords are non constrained and can be typed freely. |
| License (dataset) | The License refers to the permissions attached to a dataset regarding conditions of use, reproducibility and monetary use |
| Map builder | Map builder is the map building solution of OpenDatasoft. With Map Builder, you can quickly add datasets to a geographical view and customize the colors, data clustering methods and tooltips. |
Metadata |
Metadata are “data that provide information about other data”. Two types of metadata exist: structural metadata and descriptive metadata. Structural metadata are data about the rst-classs of data. Descriptive metadata use individual instances of application data or the data content. |
| Publisher (dataset) | The publisher is the entity responsible of the data dissemination either to the general public in Open Data or to targeted users |
Record |
A record (also called struct or compound data) is a basic data structure. A record is a collection of fields, possibly of different data types, typically in fixed number and sequence |
| Reuse | A reuse is a voluntary declaration of dataset use in another context (a map, an application, a website) by anyone |
| Subdomain | A subdomain is a child domain of a parent domain. A parent domain can distribute or collect content to these child domains. |
| Tags | Tags (or keywords) help users discover your dataset and should include terms that would be used by technical and non-technical users. |
| Theme (dataset) | A theme is a dataset topic, it helps categorize dataset into bigger categories. Themes are constrained and are to be chosen in a list. |
Technical glossary
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
API |
An application programming interface, which is a set of definitions of the ways one piece of computer software communicates with another. It is a method of achieving abstraction, usually (but not necessarily) between higher-level and lower-level software. |
API Key |
An application programming interface key (API key) is a code passed in by computer programs calling an application programming interface (API) to identify the calling program, its developer, or its user to the Web site. |
Basic Auth |
HTTP Basic authentication (BA) implementation is the simplest technique for enforcing access controls to web resources because it doesn’t require cookies, session identifiers, or login pages; rather, HTTP Basic authentication uses standard fields in the HTTP header, obviating the need for handshakes. |
CKAN (Comprehensive Knowledge Archive Network) |
CKAN stands for Comprehensive Knowledge Archive Network, an open source data management system that is the basis of the Data.gov catalog, as well as the open data catalogs of approximately 50 data hubs around the world. |
| Connector | A connector is a computer program specifically designed to connect to a data source. A data source can be another Open Data portal or a FTP server. |
CSV (comma separated value) |
A comma separated value (CSV) file is a computer data file used for implementing the organizational tool of the Comma Separated List. The CSV file is used for the digital storage of data structured in a table of lists form. Each line in the CSV file corresponds to a row in the table. Within a line, fields are separated by commas and each field belongs to one table column. |
CSW (Catalog Service for the Web) |
Catalog Service for the Web (CSW), sometimes seen as Catalog Service - Web, is a standard for exposing a catalog of geospatial records in XML on the Internet (over HTTP). The catalog is made up of records that describe geospatial data (e.g. KML), geospatial services (e.g. WMS), and related resources. |
Database |
A database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views, and other objects. |
DKAN (Drupal based CKAN) |
DKAN is an open-source data management platform |
DNS |
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical decentralized naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. |
Endpoint |
An end point indicates a specific location for accessing a service using a specific protocol and data format. |
EPSG (European Petroleum Survey Group) |
The EPSG Geodetic Parameter Dataset is a structured dataset of Coordinate Reference Systems and Coordinate Transformations [...] The geographic coverage of the data is worldwide, but it is stressed that the dataset does not and cannot record all possible geodetic parameters in use around the world. |
FTP |
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer computer files between a client and server on a computer network. |
Geocoding |
Geocoding is the computational process of transforming a postal address description to a location on the Earth’s surface |
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) |
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications. With Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and JavaScript, it forms a triad of cornerstone technologies for the World Wide Web. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and render them into multimedia web pages. |
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) |
The primary method used to convey information on the World Wide Web. HTTP is a request/response protocol between clients and servers. |
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) |
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is an open-standard format that uses human-readable text to transmit data objects consisting of attributeÐvalue pairs. It is the most common data format used for asynchronous browser/server communication (AJAJ), largely replacing XML which is used by AJAX. |
KML (Keyhole Markup Language) |
Keyhole Markup Language (KML) is an XML notation for expressing geographic annotation and visualization within Internet-based, two-dimensional maps and three-dimensional Earth browsers. |
KMZ (Keyhole Markup Zipped) |
KML files are very often distributed in KMZ files, which are zipped files with a .KMZ extension. When a KMZ file is unzipped, a single doc.kml is found along with any overlay and icon images referenced in the KML and any network-linked KML files. |
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) |
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network. |
Machine-Readable File |
Refers to information or data that is in a format that can be easily processed by a computer without human intervention while ensuring no semantic meaning is lost. |
Mapbox |
Mapbox is a large provider of custom online maps for websites such as Foursquare, Pinterest, Evernote, the Financial Times, The Weather Channel and Uber Technologies. Since 2010, it has rapidly expanded the niche of custom maps, as a response to the limited choice offered by map providers such as Google Maps. |
OAuth |
OAuth is an open standard for authorization, commonly used as a way for Internet users to log in to third party websites using their Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Twitter, One Network, etc. accounts without exposing their password. Generally, OAuth provides to clients a “secure delegated access” to server resources on behalf of a resource owner. |
oData |
Open Data Protocol (OData) is an open protocol which allows the creation and consumption of queryable and interoperable RESTful APIs in a simple and standard way |
Open Source Software |
Computer software that is available in source code form: the source code and certain other rights normally reserved for copyright holders are provided under an open-source license that permits users to study, change, improve and at times also to distribute the software.Open source software is very often developed in a public, collaborative manner. |
| Parser (or extractor) | A parser is a computer program that takes a file as input, processes and indexes it in order for the platform or people to perform complex operations on them. |
RDF (Resource Description Framework ) |
The Resource Description Framework (RDF) is a family of World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) specifications originally designed as a metadata data model. It has come to be used as a general method for conceptual description or modeling of information that is implemented in web resources, using a variety of syntax notations and data serialization formats. It is also used in knowledge management applications. |
REST (Representational state transfer) |
In computing, representational state transfer (REST) is an architectural style used for web development. Systems and sites designed using this style aim for fast performance, reliability and the ability to scale (to grow and easily support extra users). To achieve these goals, developers work with reusable components that can be managed and updated without affecting the system as a whole while it is running. |
RSS (Rich Site Summary) |
RSS (Rich Site Summary; originally RDF Site Summary; often called Really Simple Syndication) uses a family of standard web feed formats to publish frequently updated information: blog entries, news headlines, audio, video. An RSS document (called “feed”, “web feed”,or “channel”) includes full or summarized text, and metadata, like publishing date and author’s name. |
| RSS Feed | URL for an RSS feed that provides access to the dataset. |
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) |
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an XML-based, open-standard data format for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, in particular, between an identity provider and a service provider. |
Shapefile |
The shapefile format is a popular geospatial vector data format for geographic information system (GIS) software. A shapefile stores non-topological geometry and attribute information for the spatial features in a dataset. The geometry for a feature is stored as a shape comprising a set of vector coordinates. Shapefiles can support point, line, and area features. |
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) |
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a message-based protocol based on XML for accessing services on the Web. It employs XML syntax to send text commands across the Internet using HTTP. SOAP is similar in purpose to the DCOM and CORBA distributed object systems, but is more lightweight and less programming-intensive. Because of its simple exchange mechanism, SOAP can also be used to implement a messaging system. |
SQL (Structured Query Language) |
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a special-purpose programming language designed for managing data held in a relational database management system (RDBMS), or for stream processing in a relational data stream management system (RDSMS). |
SSL certificate |
A SSL certificate is an electronic document used to secure connections between websites. The certificate includes information about the key, information about its owner’s identity, and the digital signature of an entity that has verified the certificate’s contents are correct. |
Swagger |
The OpenAPI Specification (originally known as the Swagger Specification) is a specification for machine-readable interface files for describing, producing, consuming, and visualizing RESTful web services. A variety of tools can generate code, documentation and test cases given an interface file |
Tiles |
Tiles are individually requested image files over the internet that are seemlessly joined to create a map |
Token |
A token is piece of data that is used in network communications (often over HTTP) to identify a session, a series of related message exchanges. On the platform, tokens allow you to connect to external services. |
TSV (Tab Separated Values) |
A simple text format for a database table. Each record in the table is one line of the text file. Each field value of a record is separated from the next by a tab stop character. It is a form of the more general delimiter-separated values format. |
Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) |
Turtle (Terse RDF Triple Language) is a format for expressing data in the Resource Description Framework (RDF) data model with a syntax similar to SPARQL. RDF, in turn, represents information using “triples”, each of which consists of a subject, a predicate, and an object. Each of those items is expressed as a Web URI. |
Web Service |
A Web service is a service offered by an electronic device to another electronic device, communicating with each other via the World Wide Web. In a Web service, Web technology such as HTTP, originally designed for human-to-machine communication, is utilized for machine-to-machine communication, more specifically for transferring machine readable file formats such as XML and JSON. |
WFS (Web Feature Service) |
Web Feature Service Interface Standard (WFS) provides an interface allowing requests for geographical features across the web using platform-independent calls |
WSDL (Web Services Description Language) |
The Web Services Description Language is an XML-based interface definition language that is used for describing the functionality offered by a web service. |
XML (Extensible Markup Language) |
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a general-purpose specification for creating custom markup languages. It is classified as an extensible language, because it allows the user to define the mark-up elements. XML’s purpose is to aid information systems in sharing structured data especially via the Internet, to encode documents, and to serialize data. |